Build 31
Prototype
Prototypes are simulations of products or services that are created with the intention of communicating and learning without the full investment of development. While design teams are often able to refine their designs and make better decisions simply through the activity of building prototypes, the primary goal is usually to learn by sharing with stakeholders and doing user validation with your target audience.
Prototypes are most useful for testing innovative products and services and for ensuring that users understand novel interactions. They can range in fidelity from rough paper prototypes that the design team can produce quickly to full-fledged production prototypes that usually require coordination with developers or manufacturers. As the level of investment rises, typically so does the quality of the feedback. Choosing a prototype fidelity depends on how far along your project is and what you hope to learn from testing it.
Buy from Amazon Buy ElsewherePersonal Intelligence
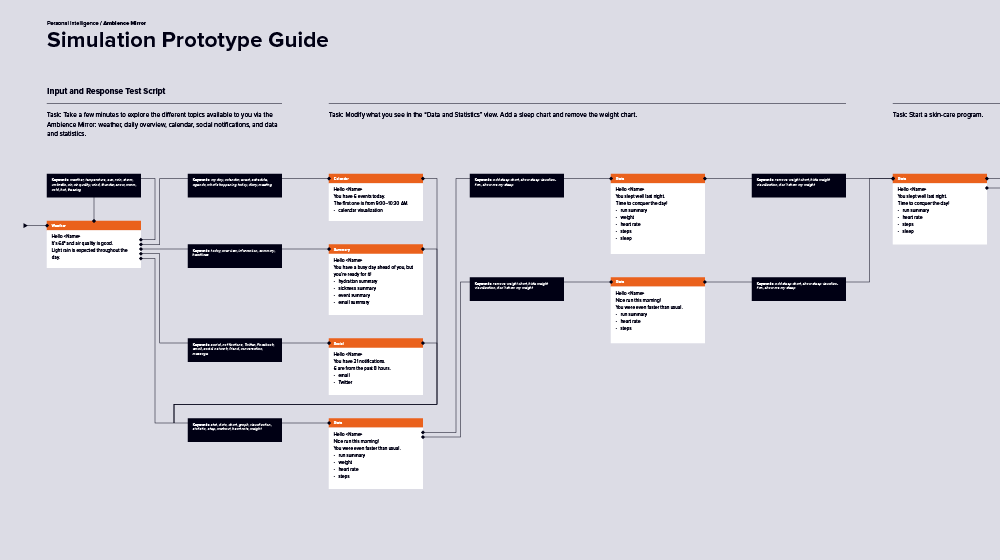
Ambience Mirror
Ambience Mirror uses multiple prototypes. A proof-of-concept prototype (not shown) is maintained throughout to confirm that all designs and integrations are possible. The mirror also relies on a simulation prototype for user validation, with a designer using a script to react to users’ voice commands.
Related Chapters
26
Motion Studies
How does the product behave over time? What feedback does the user get when interacting with the experience?
29
Detailed Design
When are we ready to dive into the details? How do we prioritize what we design for communication purposes?
30
Flow Diagram
How do we communicate a complex system without hundreds of pages of documentation?
35
User Validation
How do we make sure our product will survive in the wild? When should we seek feedback from users?